The Juicebox Podcast is featured on iTunes!
A huge thank you to Apple Podcasts and iTunes for shining a spotlight on episode #111 of the Juicebox Podcast.
Guest: Actor from 'Baby Daddy' and life-long type 1, Derek Theler...
You can listen to this and past episodes on Apple Podcast. Subscribe today!
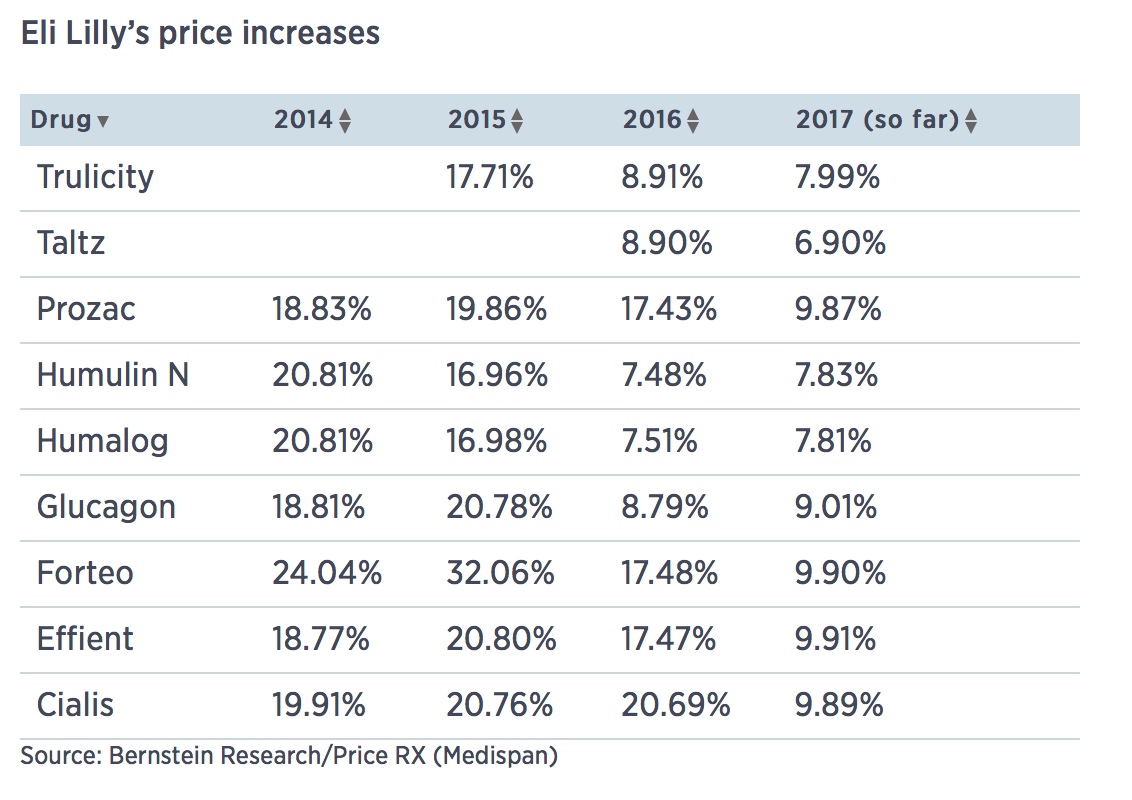
Eli Lilly raised prices on 9 drugs last week
Humalog and Humulin (7.8 percent)
Indianapolis drug giant Eli Lilly raised list prices of nine of its medicines last week between 6 and 10 percent, according to data obtained by CNBC.
The increases, taken on May 2, were for drugs including the blood thinner Effient (9.9 percent), the psoriasis drug Taltz (6.9 percent) and the insulins Humalog and Humulin (7.8 percent).
The increases fit a pattern at Lilly and many other drugmakers of single-digit percentage hikes once or twice a year, despite political pressure and intense scrutiny of the practices. Lilly has come under fire for the price of its insulin drugs in particular, leading Senator Bernie Sanders to call for a federal investigation into collusion. Lilly and other insulin makers have denied any such activity.
Lilly confirmed the price increases in an emailed statement to CNBC, and noted the list prices "do not reflect the significant discounts and rebates that we provide to ensure patients have adequate access to our medicines."
"The net price increase that Lilly recognizes is significantly less," spokesman Mark Taylor wrote. "In fact, in 2016, the average discount to list price on our U.S. portfolio rose to 50 percent and net prices rose just 2.4 percent in the U.S."
You can read the entire article on CNBC
Little Girls are like Snowflakes
Little girls are like snowflakes, no two are exactly the same...
Snow day! It is snowing here as I write this post which is strange because it was sixty-five degrees yesterday afternoon when Arden came home from school and asked me this question.
"Can I have a sleepover tonight if school gets cancelled tomorrow because of snow?".
I thought for a moment and decided that if Arden had friends overnight then they would stay up late and if they stayed up late... then they would sleep in. I immediately imagined a morning to myself, smiled and said "sure!".
The sleepover brought one surprise that I hadn't pre-planned for, I needed more food at dinner time then I had in the house and so we ordered out. When the pizza, fries and some other stuff arrived at the door we bolused, set an increased temp basal and Arden ate. About an hour later her BG began to slowly drift up. I had been noticing all day that her BG wasn't responding to boluses the way I expected and began considering if we needed a new pump site. An hour later after I wasn't getting the movement that I wanted (her BG was 160) Arden changed her pump.
I was aggressive with the insulin after the site change because of the new infusion, pizza in her belly and the excitement of a sleepover. Still around midnight her BG was still stuck at 150. When I went into Arden's room the three girls were passed out on an inflatable mattress that they set up next to Arden's bed. So it was air mattress on the far side of the room, then Arden's bed, then me. I was farthest from the air mattress because of where Arden's Omnipod PDM was located. I clicked a few buttons sent a bolus to her pod (it has great range) and went back to bed.
Not ten minutes later I decided that I should have also used an increased temp basal rate and so I snuck back in to the room. It was dark but I could see that Arden had made her way from the air mattress and was now sleeping in her bed. I crouched down next to her and held the wireless PDM close to her abdomen where she had recently put her new pod. The PDM couldn't connect. I tried again, wouldn't connect. I jammed the PDM between Arden and the mattress... nothing. As I began to worry that the new pod might not be working correctly Arden jumped up in the darkness, I had scared her. This felt wrong as she has never responded in the middle of the night like that. As I was about to ask if she was okay a voice said, "Sorry you scared me... Mr. B... I'm not Arden".
So it turns out that Nadia, Arden's friend was the one who moved from the air mattress to Arden's bed and the reason I couldn't connect to Arden's pod? It was across the room and Nadia's body was absorbing the signal.
We don't get too many middle of the night insulin related laughs around here and I imagine that you don't either so I wanted to share. I have to remember to tell this story on the podcast sometime. I felt like an idiot.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
Today, I am begrudgingly breaking a long standing rule on this blog of not talking about politics...
Betsy DeVos
Yesterday a new Education Secretary, Betsy DeVos, was confirmed by the Senate. DeVos a wealthy Republican donor who never attended a public school, is not an educator and has spent most of her life promoting charter schools and vouchers is now in charge of almost 100,000 public schools.
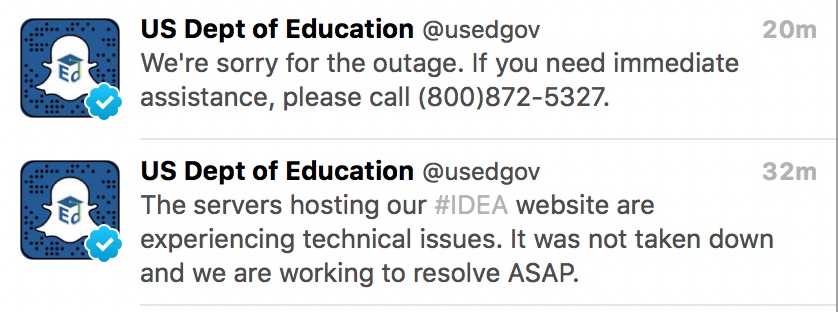
Today the government website for the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act is not responding...
I'm going to go out on a limb and say if it looks like a duck and quacks like a duck, you better start calling your Senators and Congresspeople.
About IDEA from the ADA website
What is IDEA?
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is a federal law that requires states to provide a "free, appropriate public education" to children with disabilities so they can be educated to the greatest extent possible along with all other children. Qualifying children are entitled to special education and related services at no cost to their parents/guardians.
Who is covered?
To receive services under IDEA, a child with with a disability must show that he or she needs special education and related services in order to benefit from education. An evaluation of the child must show that, because of the child's disability, the child's educational performance is harmed. There are three situations in which a child with diabetes might be covered under IDEA:
1. The child has another disability which impacts his or her ability to learn, but diabetes itself does not cause an impact in learning. For example, a child with Down syndrome might have an impact in learning.
2. Both diabetes and another disability combined impact the child's ability to learn. For example, it might be determined that a child's ability to learn is impacted by both autism and diabetes.
3. The child's diabetes, by itself, causes an impact on learning. This is categorized as an "other health impairment" under the IDEA.
While it is most common for a child with diabetes to qualify for IDEA because of having another disability in addition to diabetes, it is also possible that diabetes itself can cause an impact in learning. For example, it is often difficult to learn when blood sugar levels are either too high or too low. If a child with diabetes is having difficulty managing his or her blood sugar level, this may hurt how well the child does in school. Academic progress might also suffer if a child with diabetes misses a significant amount of classroom instruction each day in order to attend to diabetes care tasks.
The Center for Parent Information and Resources describes "Other Health Impairments" like this.
“Other Health Impairment” is one of the 14 categories of disability listed in our nation’s special education law, the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). Under IDEA, a child who has an “other health impairment” is very likely to be eligible for special services to help the child address his or her educational, developmental, and functional needs resulting from the disability.
(i) Is due to chronic or acute health problems such as asthma, attention deficit disorder or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, diabetes, epilepsy, a heart condition, hemophilia, lead poisoning, leukemia, nephritis, rheumatic fever, sickle cell anemia, and Tourette syndrome; and
You can read the rest on their website here.
update 9:54am - Dept of Ed says this is not purposeful.
President Obama's Piece for the New England Journal Of Medicine
This piece from President Obama was published in the New England Journal of Medicine on January 26, 2017. Next week on the Juicebox Podcast I'll be highlighting three people living with type 1 diabetes, they will each be sharing their experience with the Affordable Care Act. - Scott
Repealing the ACA without a Replacement — The Risks to American Health Care
Barack H. Obama, J.D.
N Engl J Med 2017; 376:297-299 January 26, 2017 DOI: 10.1056/NEJMp1616577
Health care policy often shifts when the country’s leadership changes. That was true when I took office, and it will likely be true with President-elect Donald Trump. I am proud that my administration’s work, through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and other policies, helped millions more Americans know the security of health care in a system that is more effective and efficient. At the same time, there is more work to do to ensure that all Americans have access to high-quality, affordable health care. What the past 8 years have taught us is that health care reform requires an evidence-based, careful approach, driven by what is best for the American people. That is why Republicans’ plan to repeal the ACA with no plan to replace and improve it is so reckless. Rather than jeopardize financial security and access to care for tens of millions of Americans, policymakers should develop a plan to build on what works before they unravel what is in place.
Thanks to the ACA, a larger share of Americans have health insurance than ever before. Increased coverage is translating into improved access to medical care — as well as greater financial security and better health. Meanwhile, the vast majority of Americans still get their health care through sources that predate the law, such as a job or Medicare, and are benefiting from improved consumer protections, such as free preventive services.
We have also made progress in how we pay for health care, including rewarding providers who deliver high-quality care rather than just a high quantity of care. These and other reforms in the ACA have helped slow health care cost growth to a fraction of historical rates while improving quality for patients. This includes better-quality and lower-cost care for tens of millions of seniors, individuals with disabilities, and low-income families covered by Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program. And these benefits will grow in the years to come.
That being said, I am the first to say we can make improvements. Informed by the lessons we’ve learned during my presidency, I have put forward ideas in my budgets and a July 2016 article to address ongoing challenges — such as a lack of choice in some health insurance markets, premiums that remain unaffordable for some families, and high prescription-drug costs. For example, allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices could both reduce seniors’ spending and give private payers greater leverage. And I have always welcomed others’ ideas that meet the test of making the health system better. But persistent partisan resistance to the ACA has made small as well as significant improvements extremely difficult.
Now, Republican congressional leaders say they will repeal the ACA early this year, with a promise to replace it in subsequent legislation — which, if patterned after House Speaker Paul Ryan’s ideas, would be partly paid for by capping Medicare and Medicaid spending. They have yet to introduce that “replacement bill,” hold a hearing on it, or produce a cost analysis — let alone engage in the more than a year of public debate that preceded passage of the ACA. Instead, they say that such a debate will occur after the ACA is repealed. They claim that a 2- or 3-year delay will be sufficient to develop, pass, and implement a replacement bill.
This approach of “repeal first and replace later” is, simply put, irresponsible — and could slowly bleed the health care system that all of us depend on. (And, though not my focus here, executive actions could have similar consequential negative effects on our health system.) If a repeal with a delay is enacted, the health care system will be standing on the edge of a cliff, resulting in uncertainty and, in some cases, harm beginning immediately. Insurance companies may not want to participate in the Health Insurance Marketplace in 2018 or may significantly increase prices to prepare for changes in the next year or two, partly to try to avoid the blame for any change that is unpopular. Physician practices may stop investing in new approaches to care coordination if Medicare’s Innovation Center is eliminated. Hospitals may have to cut back services and jobs in the short run in anticipation of the surge in uncompensated care that will result from rolling back the Medicaid expansion. Employers may have to reduce raises or delay hiring to plan for faster growth in health care costs without the current law’s cost-saving incentives. And people with preexisting conditions may fear losing lifesaving health care that may no longer be affordable or accessible.
Furthermore, there is no guarantee of getting a second vote to avoid such a cliff, especially on something as difficult as comprehensive health care reform. Put aside the scope of health care reform — the federal health care budget is 50% bigger than that of the Department of Defense. Put aside how it personally touches every single American — practically every week, I get letters from people passionately sharing how the ACA is working for them and about how we can make it better. “Repeal and replace” is a deceptively catchy phrase — the truth is that health care reform is complex, with many interlocking pieces, so that undoing some of it may undo all of it.
Take, for example, preexisting conditions. For the first time, because of the ACA, people with preexisting conditions cannot be denied coverage, denied benefits, or charged exorbitant rates. I take my successor at his word: he wants to maintain protections for the 133 million Americans with preexisting conditions. Yet Republicans in Congress want to repeal the individual-responsibility portion of the law. I was initially against this Republican idea, but we learned from Massachusetts that individual responsibility, alongside financial assistance, is the only proven way to provide affordable, private, individual insurance to every American. Maintaining protections for people with preexisting conditions without requiring individual responsibility would cost millions of Americans their coverage and cause dramatic premium increases for millions more. This is just one of the many complex trade-offs in health care reform.
Given that Republicans have yet to craft a replacement plan, and that unforeseen events might overtake their planned agenda, there might never be a second vote on a plan to replace the ACA if it is repealed. And if a second vote does not happen, tens of millions of Americans will be harmed. A recent Urban Institute analysis estimated that a likely repeal bill would not only reverse recent gains in insurance coverage, but leave us with more uninsured and uncompensated care than when we started.
Put simply, all our gains are at stake if Congress takes up repealing the health law without an alternative that covers more Americans, improves quality, and makes health care more affordable. That move takes away the opportunity to build on what works and fix what does not. It adds uncertainty to lives of patients, the work of their doctors, and the hospitals and health systems that care for them. And it jeopardizes the improvements in health care that millions of Americans now enjoy.
Congress can take a responsible, bipartisan approach to improving the health care system. This was how we overhauled Medicare’s flawed physician payment system less than 2 years ago. I will applaud legislation that improves Americans’ care, but Republicans should identify improvements and explain their plan from the start — they owe the American people nothing less.
Health care reform isn’t about a nameless, faceless “system.” It’s about the millions of lives at stake — from the cancer survivor who can now take a new job without fear of losing his insurance, to the young person who can stay on her parents’ insurance after college, to the countless Americans who now live healthier lives thanks to the law’s protections. Policymakers should therefore abide by the physician’s oath: “first, do no harm.”
The Massachusetts Medical Society copyright applies to the distinctive display of this New England Journal of Medicine article and not to the President’s work or words.
This article was published on January 6, 2017, at NEJM.org.
SOURCE INFORMATION
Mr. Obama is the former President of the United States.